What is MQTT? A Complete Guide for Beginners
January 30, 2026
What is MQTT? A Complete Guide for Beginners
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight and efficient messaging protocol designed for the Internet of Things (IoT). It excels in scenarios where devices have limited resources and network bandwidth is at a premium. Originally developed to monitor oil pipelines, it has become the gold standard for real-time, reliable communication in a vast range of IoT and IIoT applications.
This guide serves as a central pillar to understanding MQTT. We will cover the core concepts and provide links to deep-dive articles on specific sub-topics to give you a complete and comprehensive overview.
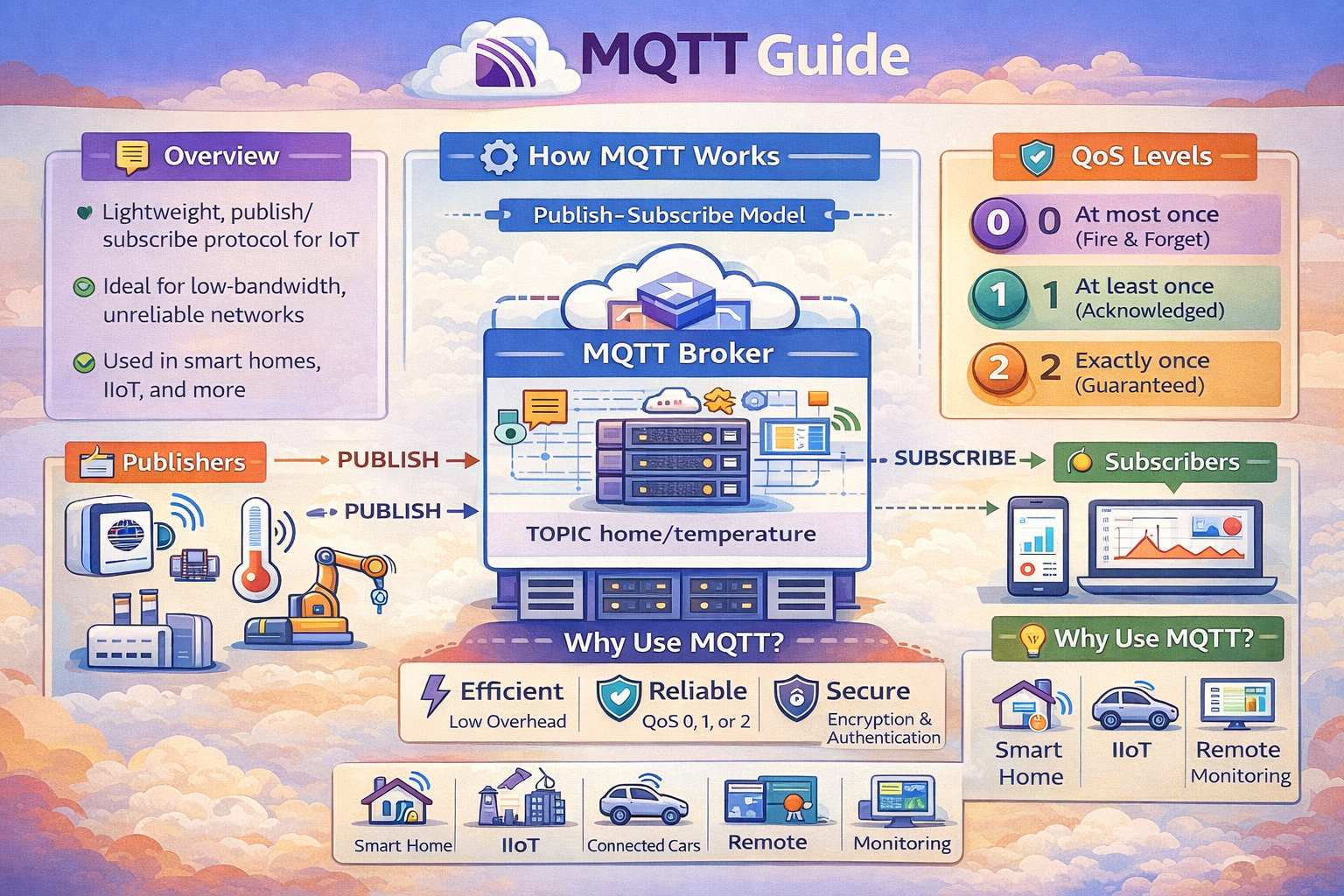
The Publish-Subscribe Architecture
Unlike the request-response model of HTTP, MQTT uses a publish-subscribe (pub-sub) pattern. This architecture brilliantly decouples the message sender (the publisher) from the receiver (the subscriber) using a central hub called a broker.
The core of this model involves three components: Publishers, Subscribers, and a Broker. Publishers are clients that send messages, subscribers are clients that receive them, and the broker is the intermediary that routes messages based on topics. This decoupling of space, time, and synchronization is what makes the system so flexible and scalable.
- To learn more about how clients, topics, and wildcards work, read our full guide on Understanding the MQTT Client Publish-Subscribe Model.
The Central Role of the MQTT Broker
The MQTT Broker is the heart of the system. It is a central server responsible for receiving all messages from publishing clients and routing them to the correct subscribing clients. It manages client connections, handles security, and ensures reliable message delivery based on the rules of the protocol.
Choosing the right broker is critical for the stability, performance, and scalability of any IoT project. Modern brokers are highly sophisticated pieces of software, designed for high availability and massive throughput.
- For a comprehensive overview of broker functionalities, read our Deep Dive into the MQTT Broker.
- To explore cutting-edge broker technology, see our article on Next-Generation MQTT Brokers: Synapse.
Quality of Service (QoS): Guaranteeing Message Delivery
To operate effectively on unreliable networks, MQTT provides three levels of Quality of Service (QoS). This is a crucial feature that allows developers to choose the right trade-off between performance and reliability for each specific message.
| QoS Level | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | At Most Once | The fastest level, but with no guarantee of delivery. |
| 1 | At Least Once | Guarantees the message will be delivered, but it might arrive more than once. |
| 2 | Exactly Once | The most reliable (and slowest) level, guaranteeing the message is delivered exactly once. |
- For a detailed explanation of how each level works and when to use them, check out MQTT QoS Explained (0, 1, & 2).
MQTT vs. HTTP: Why Choose MQTT for IoT?
While HTTP is the backbone of the web, it is often too heavy and inefficient for IoT. Its request-response, high-overhead nature is not suited for resource-constrained devices or real-time data streaming. MQTT was designed from the ground up to solve these problems. It uses a persistent connection, has a tiny message header, and its pub-sub model eliminates the need for constant polling, saving battery life and bandwidth.
- Read our detailed breakdown of the differences in our MQTT vs. HTTP for IoT article.
Core MQTT Use Cases & Applications
MQTT's flexibility has made it a cornerstone of modern IoT deployments across numerous industries.
1. Industrial IoT (IIoT) and SCADA
In the industrial world, MQTT is used to connect sensors, PLCs, and other machinery to SCADA systems and cloud platforms. Its efficiency and reliability are essential for real-time monitoring and control. An important extension for this space is Sparkplug B, which defines a standard topic namespace and payload format to ensure interoperability between industrial devices.
- Learn more about its industrial impact in our guide on the Role of MQTT in IIoT and SCADA.
- Discover the industrial standard for interoperability with MQTT Sparkplug B Explained.
2. Smart Home Automation
From smart lighting to temperature sensors, MQTT allows various smart home devices from different manufacturers to communicate with a central hub and with each other seamlessly. Its low latency is perfect for responsive user experiences.
- Explore practical examples in our guide on How to Use MQTT for Smart Home Automation.
Getting Hands-On with MQTT
The best way to learn is by doing. You can get started with MQTT using affordable and powerful hardware.
- Set up your own central broker at home by following our guide to using a Raspberry Pi as an MQTT Broker.
- Learn to program a popular IoT microcontroller to send sensor data with our tutorial on Getting Started with ESP32 and MQTT.