MQTT Sparkplug B: A Game-Changer for Industrial Messaging
January 30, 2026
MQTT Sparkplug B: A Game-Changer for Industrial Messaging
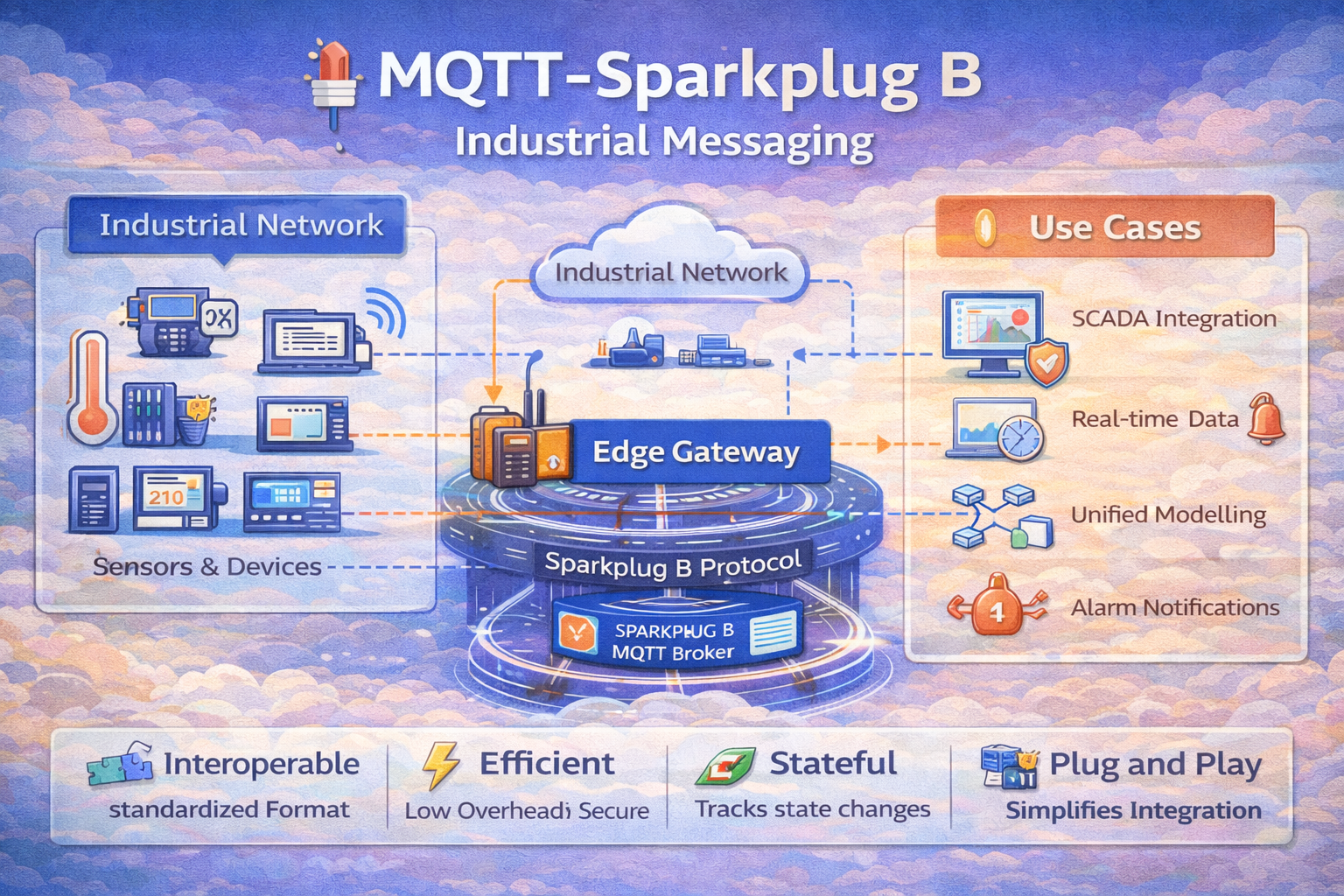
While MQTT is a powerful and lightweight protocol, its core specification is topic and payload agnostic. This can lead to a lack of interoperability in complex industrial systems. Sparkplug B is an open-source software specification that builds on top of MQTT to solve this problem.
Sparkplug B defines a standardized topic namespace, payload structure, and session state management, making it purpose-built for Industrial IoT (IIoT) and SCADA systems.
The Three Core Problems Sparkplug B Solves
- Lack of Standardization: In plain MQTT, custom parsing is required for every device type.
- Statelessness: A new application connecting to a broker doesn't know which devices are online or their current states.
- Inefficiency: Publishing every data point, even if it hasn't changed, is inefficient.
Key Components of the Sparkplug B Specification
Sparkplug defines a specific architecture and set of message types to run over a standard MQTT broker.
- SCADA/IIoT Host: The primary application that consumes and commands data.
- Edge of Network (EoN) Node: A gateway or intelligent device that acts as the bridge between legacy devices and the MQTT network. It is the primary data publisher.
Standardized Topic Namespace and Payload
Sparkplug defines a strict topic structure: namespace/group_id/message_type/eon_node_id/[device_id]
The payload is a highly efficient binary format defined by Google Protocol Buffers (Protobuf), which includes a timestamp and a list of "metrics" (the data points).
Stateful Awareness through Birth & Death Certificates
This is the most powerful feature of Sparkplug.
- Birth Certificates (
BIRTH): When a device comes online, it publishes a "birth certificate" message containing a complete list of all its metrics and their current values. The SCADA host application subscribes to these topics and immediately knows the device is online and has a full data image. - Death Certificates (
DEATH): Using MQTT's built-in Last Will and Testament (LWT) feature, a "death certificate" is published automatically if a device disconnects ungracefully. This allows the host to immediately mark all associated data as stale.
By combining stateful awareness with report-by-exception, Sparkplug B provides a robust and interoperable solution for industrial messaging built on the flexible foundation of the MQTT publish-subscribe model.