The Role of MQTT in Modern IIoT and SCADA Systems
January 30, 2026
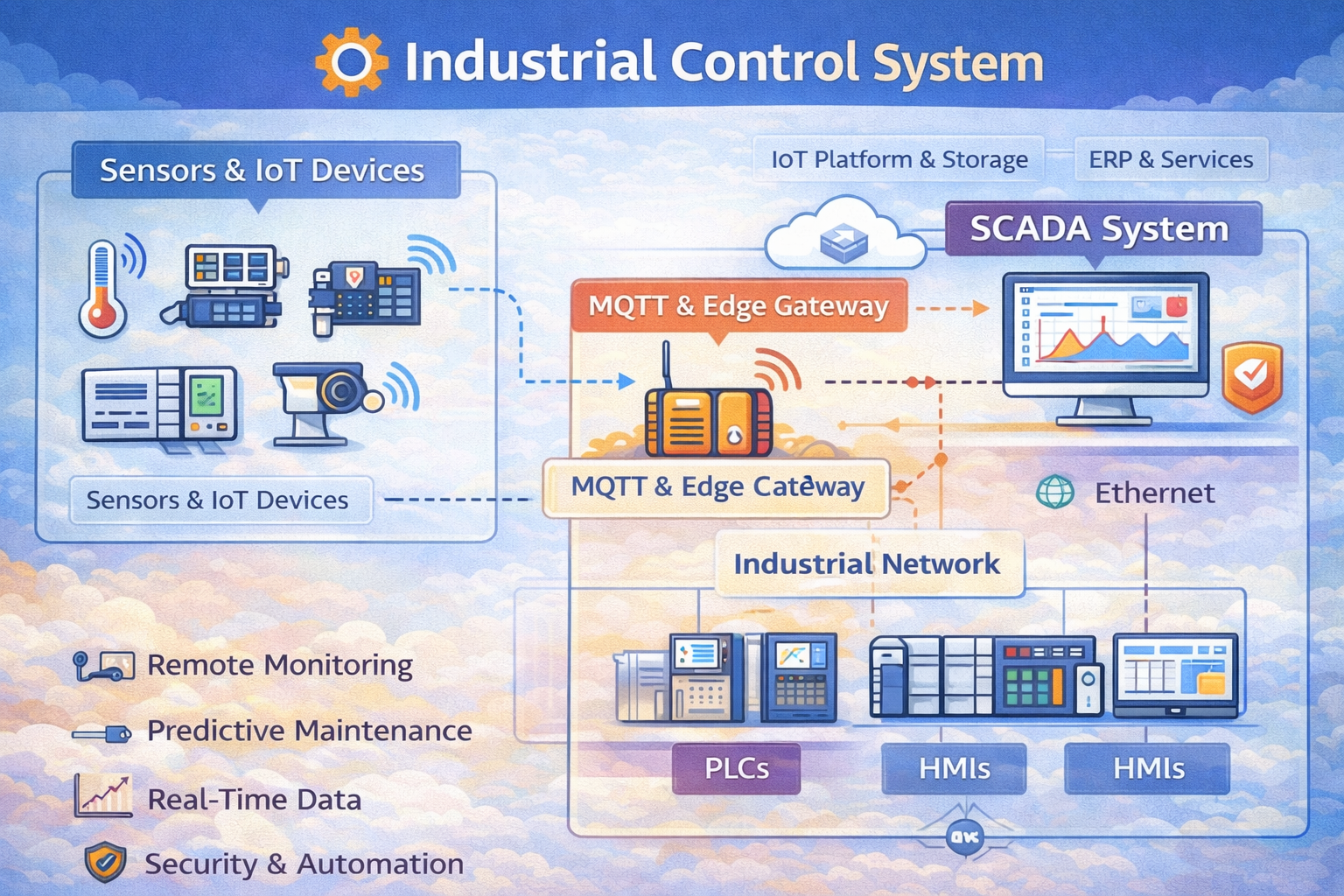
The Evolving Role of MQTT in IIoT and SCADA Systems
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems have been the backbone of industrial control for decades. Traditionally, these systems relied on proprietary, poll-response protocols. While robust, they face challenges in the era of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which demands connectivity, scalability, and security.
MQTT, with its modern publish-subscribe architecture, has emerged as a critical technology for bridging the gap between legacy Operational Technology (OT) and modern Information Technology (IT) infrastructure.
Why MQTT is the Perfect Bridge for IIoT
Traditional industrial protocols are often heavy or based on an inefficient polling model. MQTT, with its lightweight and publish-subscribe model, solves many of these problems.
| Feature | Industrial Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lightweight Header | Minimizes bandwidth usage on factory networks. |
| Pub/Sub Model | A single PLC can publish its data once, and it can be consumed by multiple systems without extra load on the PLC. |
| Report-by-Exception | Devices only publish messages when their state changes, drastically reducing network traffic. |
| State Awareness | The Last Will and Testament (LWT) feature immediately notifies the system if a critical machine goes offline. |
Architecture: Integrating MQTT with SCADA
A common architecture involves using an MQTT broker as a central data bus. An Edge Gateway on the factory floor subscribes to sensor data and then publishes it to the central broker.
The Next Step: MQTT Sparkplug B
To further enhance MQTT for industrial use, the Sparkplug B specification was created. It provides a standardized topic namespace and payload structure, ensuring interoperability between devices and applications from different vendors.