The Next Generation of MQTT Brokers: Agentic Architecture with Synapse
January 30, 2026
The Next Generation of MQTT Brokers: Agentic Architecture
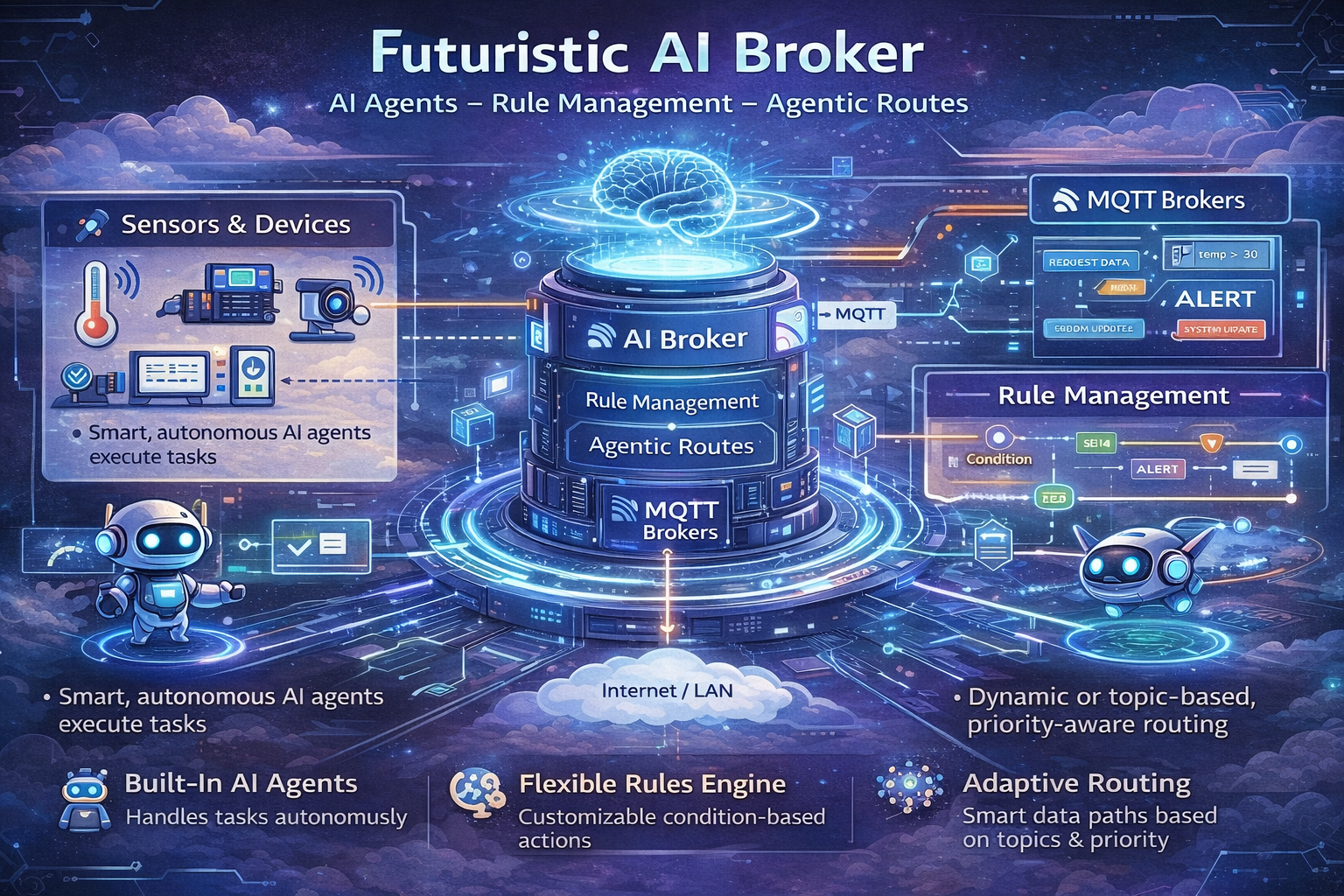
For years, the MQTT broker has served as a simple, reliable message bus: a post office that dutifully forwards messages from publishers to subscribers based on topic names. While effective, this model is passive. The broker has no understanding of the content of the messages it handles. As IoT systems become more complex, there is a growing need for intelligence within the messaging layer itself.
This need gives rise to the next generation of MQTT infrastructure: the Agentic Broker. An agentic broker, like the upcoming MQTTfy Synapse, embeds an AI agent core directly into the message processing pipeline, transforming it from a passive router into an active, intelligent hub.
From Passive Router to Intelligent Hub
A traditional MQTT broker's logic is simple: IF topic matches subscription, THEN forward message. An agentic broker introduces a powerful new paradigm.
The workflow becomes:
- Ingest: The broker receives a message on a topic.
- Trigger: Instead of immediately looking for subscribers, the broker triggers a dedicated AI agent associated with that topic or data source.
- Analyze & Act: The AI agent analyzes the message's payload. Based on its pre-defined goal and the tools at its disposal, it can perform complex actions:
- Data Validation: Check if the payload conforms to a required schema. If not, it can reject the message or route it to an error topic.
- Contextual Enrichment: Use a "tool" to call an external API. For example, it could take a GPS coordinate, call a reverse-geocoding API to get a street address, and append that address to the message payload.
- AI-Powered Analysis: Use a "tool" to pass the data to a larger language model (LLM) or a specialized machine learning model for anomaly detection, classification, or prediction.
- Intelligent Routing: Based on the outcome of its analysis, the agent makes a routing decision. A message with an anomalous reading might be published to
alerts/critical, while normal readings go totelemetry/standard.
Use Cases for an Agentic Broker
The possibilities are transformative.
1. Broker-Level Anomaly Detection: An AI agent within the broker can maintain a running average of sensor values. If a new message comes in that is a statistical outlier, the agent can reroute it to a high-priority alerts/anomaly topic or trigger an immediate action, even before the data hits a database.
2. Dynamic Data Transformation: Imagine a US-based application and a Europe-based application are both subscribed to a temperature sensor that publishes in Celsius. The agentic broker can detect which client is which and automatically transform the payload to Fahrenheit for the US client while leaving it as Celsius for the European one.
3. Centralized Business Logic: In the smart factory example above, the intelligence is centralized. The subscribing applications (like a dashboard) don't need complex logic; they simply subscribe to the alerts/# topic and display the pre-processed, actionable information provided by the agent. This dramatically simplifies client applications and reduces maintenance.
Key Advantages of Agentic Architecture
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| In-Stream Processing | Logic is applied as data flows through the broker, not after it reaches its destination. | Reduces latency, centralizes business logic, and ensures data is validated and enriched at the source. |
| Decoupled Intelligence | The data-producing device is dumb; the intelligence resides in the broker. | Devices can be simple and low-cost. Business logic can be updated in the broker without touching device firmware. |
| Tool-Based Extensibility | AI agents can be granted "tools" to interact with any external system via API or database query. | Infinitely extensible. The broker can become the central nervous system connecting OT and IT systems. |
| Stateful Routing | Routing decisions can be based on historical data or external state, not just the current message. | Enables more complex and context-aware automations, moving closer to true autonomous operations. |
The shift towards agentic brokers represents a fundamental change in how we think about messaging infrastructure. It's no longer just about delivering data, but about understanding, enriching, and acting on that data in real-time, paving the way for more intelligent, responsive, and autonomous systems.