How to Set Up a Raspberry Pi as an MQTT Broker
January 30, 2026
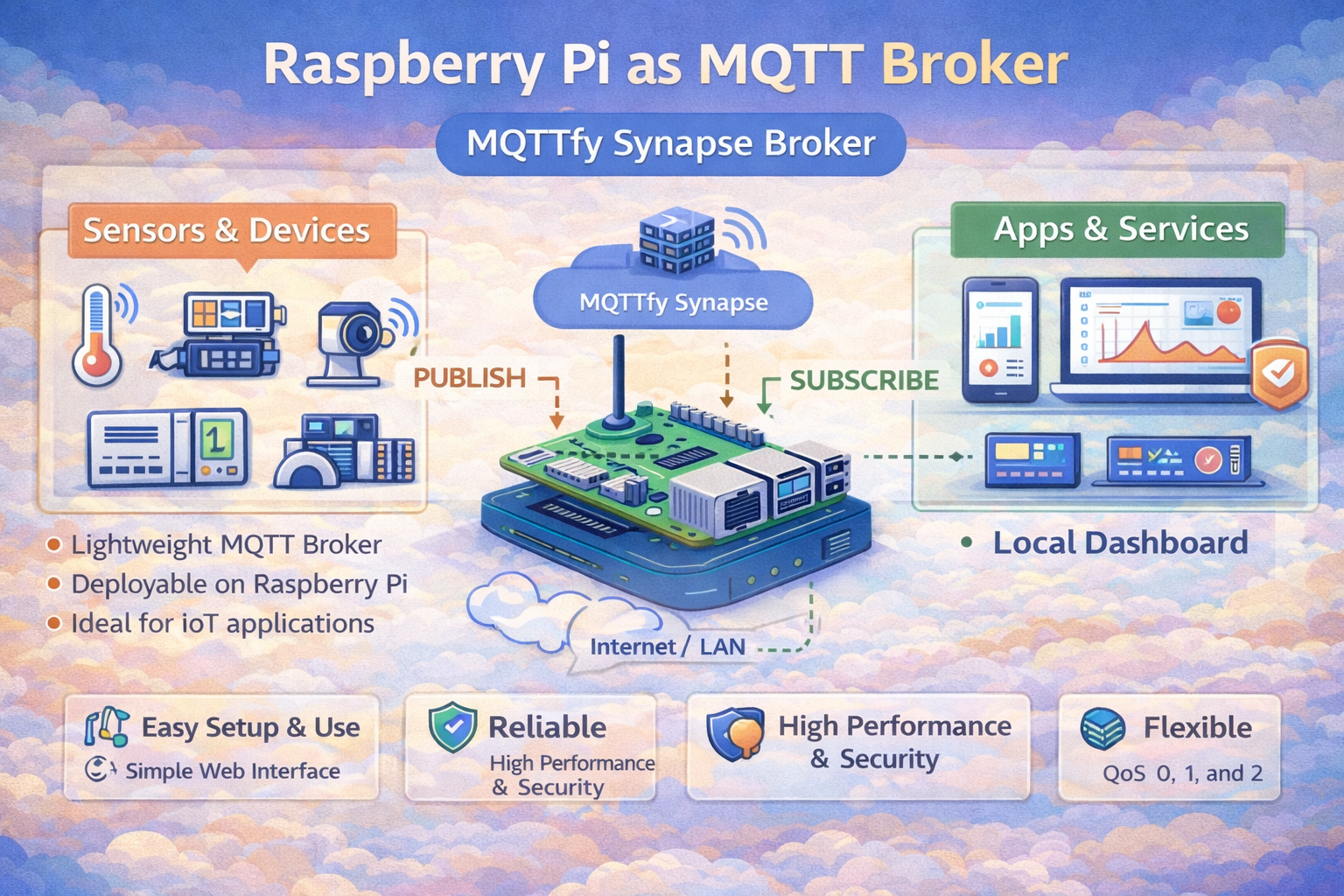
Building Your Own IoT Hub: Setting Up a Raspberry Pi as an MQTT Broker
For any smart home or IoT project built on the MQTT protocol, having a local, reliable broker is a game-changer. It puts you in control of your data, reduces reliance on cloud services, and provides near-instantaneous communication between your devices. A Raspberry Pi is the perfect device for this task: it's low-power, affordable, and more than capable of handling a typical home's MQTT traffic.
This guide will walk you through installing and configuring Mosquitto, one of the most popular open-source MQTT brokers, on your Raspberry Pi.
Prerequisites
- A Raspberry Pi (Model 3B+ or newer recommended).
- Raspberry Pi OS installed and configured on an SD card.
- Access to your Raspberry Pi's terminal (directly or via SSH).
Step 1: Update Your System
Always start by ensuring your system's package lists are up to date.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Install Mosquitto
Mosquitto and its command-line clients are available in the standard repositories.
# Install the Mosquitto broker and the command-line clients
sudo apt install mosquitto mosquitto-clients -y
Once installed, the broker will start automatically. You can enable it to ensure it always starts on boot with sudo systemctl enable mosquitto.
Step 3: Basic Security Configuration
Running an open broker is a security risk. At a minimum, you must set up username and password authentication.
-
Create a Password File: Use the
mosquitto_passwdutility to create a password file. The-cflag creates the file; omit it when adding more users later.# Replace 'myuser' with your desired username sudo mosquitto_passwd -c /etc/mosquitto/passwd myuser -
Create a Configuration File: Tell the broker to use your password file.
# Create and edit a new config file sudo nano /etc/mosquitto/conf.d/default.confAdd the following lines:
allow_anonymous false password_file /etc/mosquitto/passwd -
Restart the Broker: Apply the new configuration.
sudo systemctl restart mosquitto
Step 4: Testing Your Broker
Now, test the setup using the command-line clients. These tools are fundamental to understanding the publish-subscribe model.
-
In one terminal (Subscriber):
# Replace 'myuser' and 'mypassword' with your credentials mosquitto_sub -h localhost -t "test/topic" -u "myuser" -P "mypassword" -
In a second terminal (Publisher):
# Replace 'myuser' and 'mypassword' with your credentials mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t "test/topic" -m "Hello from Raspberry Pi!" -u "myuser" -P "mypassword"
If successful, the message will appear in the subscriber terminal. You now have a working MQTT hub!
Next Steps
Your broker is ready. The next logical steps are:
- Configure Your Devices: Point your IoT devices, like those based on an ESP32, to your Pi's IP address.
- Improve Reliability: Understand how different Quality of Service levels affect message delivery.
- Visualize Data: Connect a dashboard application to monitor your IoT data in real-time.