Wireless Home Automation: Control Relays with ESP32 and MQTTfy Dashboard
November 21, 2025
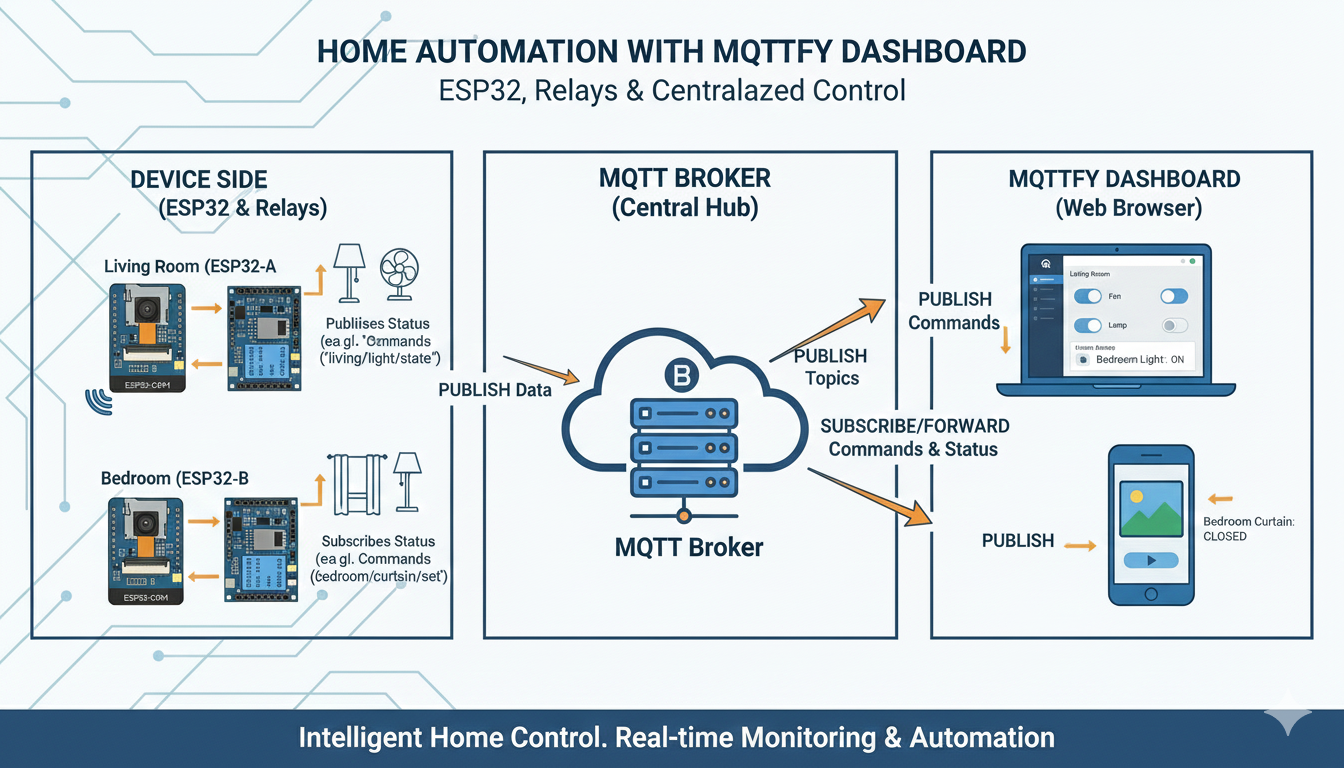
Controlling your home appliances wirelessly is a cornerstone of modern smart homes. This guide will walk you through creating a powerful and flexible home automation system using the versatile ESP32 microcontroller, a relay module, and the MQTTfy dashboard. You'll learn how to control relays from a web interface, and even use voice commands through the AI assistant to turn your devices on and off. This project is perfect for beginners and experienced makers alike, providing a solid foundation for more advanced smart home projects.
Core Concepts
- ESP32: A low-cost, low-power microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, making it ideal for IoT projects.
- Relay Module: An electrically operated switch that allows a low-power signal from the ESP32 to control a high-power circuit, like a lamp or fan.
- MQTT: A lightweight messaging protocol perfect for IoT. The ESP32 will publish its status and subscribe to commands via an MQTT broker.
- MQTTfy Dashboard: Our web-based client that will provide a user interface with buttons to send commands and indicators to show the relay status.
- IoT Agent (AI Assistant): A voice-enabled assistant within MQTTfy that can understand commands like "turn on the living room light" and translate them into MQTT messages.
Hardware & Software Requirements
Hardware:
- ESP32 Development Board (e.g., NodeMCU-32S)
- 2-Channel Relay Module (or more, depending on your needs)
- Jumper Wires
- Micro-USB cable for programming
- A lamp, fan, or other appliance to control.
- An MQTT Broker (e.g., HiveMQ, Mosquitto, or a cloud-based service)
Software:
- Arduino IDE with the ESP32 board manager installed.
- MQTTfy Dashboard account.
- A modern web browser.
Circuit Diagram
The wiring is straightforward. The ESP32 will control the relay module by sending a HIGH or LOW signal to its input pins. The relay, in turn, will switch the main power to your appliance.

Wiring Instructions:
- Connect the ESP32's GND to the relay module's GND.
- Connect the ESP32's VIN (or 5V pin) to the relay module's VCC.
- Connect GPIO 23 on the ESP32 to the IN1 pin on the relay module.
- Connect GPIO 22 on the ESP32 to the IN2 pin on the relay module.
- Caution: For the high-voltage side, carefully connect the "live" wire of your appliance's power cord through the COM and NO (Normally Open) terminals of one of the relays. Always ensure the appliance is unplugged from the wall when wiring the high-voltage side.
Arduino IDE Code for ESP32
This code connects the ESP32 to your Wi-Fi and MQTT broker. It subscribes to command topics and publishes status updates.
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <PubSubClient.h>
// WiFi & MQTT Configuration
const char* ssid = "YOUR_WIFI_SSID";
const char* password = "YOUR_WIFI_PASSWORD";
const char* mqtt_server = "YOUR_MQTT_BROKER_URL";
const int mqtt_port = 1883; // Change if needed
// Relay Pins
const int relay1Pin = 23;
const int relay2Pin = 22;
// MQTT Topics
const char* relay1_command_topic = "home/livingroom/light/command";
const char* relay1_status_topic = "home/livingroom/light/status";
const char* relay2_command_topic = "home/bedroom/fan/command";
const char* relay2_status_topic = "home/bedroom/fan/status";
WiFiClient espClient;
PubSubClient client(espClient);
void setup_wifi() {
delay(10);
Serial.println();
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
}
void publishStatus(const char* topic, int state) {
client.publish(topic, state == HIGH ? "ON" : "OFF", true);
}
void callback(char* topic, byte* payload, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("Message arrived [");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print("] ");
String message;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
message += (char)payload[i];
}
Serial.println(message);
int state = -1;
if (message == "ON" || message == "1") {
state = HIGH;
} else if (message == "OFF" || message == "0") {
state = LOW;
}
if (state != -1) {
if (strcmp(topic, relay1_command_topic) == 0) {
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, state);
publishStatus(relay1_status_topic, state);
} else if (strcmp(topic, relay2_command_topic) == 0) {
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, state);
publishStatus(relay2_status_topic, state);
}
}
}
void reconnect() {
while (!client.connected()) {
Serial.print("Attempting MQTT connection...");
String clientId = "ESP32-HomeAutoClient-";
clientId += String(random(0xffff), HEX);
if (client.connect(clientId.c_str())) {
Serial.println("connected");
client.subscribe(relay1_command_topic);
client.subscribe(relay2_command_topic);
publishStatus(relay1_status_topic, digitalRead(relay1Pin));
publishStatus(relay2_status_topic, digitalRead(relay2Pin));
} else {
Serial.print("failed, rc=");
Serial.print(client.state());
Serial.println(" try again in 5 seconds");
delay(5000);
}
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(relay1Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(relay2Pin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(relay1Pin, LOW);
digitalWrite(relay2Pin, LOW);
setup_wifi();
client.setServer(mqtt_server, mqtt_port);
client.setCallback(callback);
}
void loop() {
if (!client.connected()) {
reconnect();
}
client.loop();
}
Setting Up the MQTTfy Dashboard
Now, let's create the interface on MQTTfy to control our relays.
1. Create Widgets with the AI Assistant: Open your MQTTfy dashboard and activate the IoT Agent by clicking the icon. Use the following prompts:
- "Add a button to control the living room light. The topic is
home/livingroom/light/commandand the ON value isON." - "Now add a status LED for the living room light. The topic is
home/livingroom/light/status." - "Create a button for the bedroom fan on topic
home/bedroom/fan/command." - "Also add an LED to show the fan's status on topic
home/bedroom/fan/status."
The AI will create and configure the four widgets for you. You can now use these buttons to toggle your relays!
2. Voice Control with the AI Assistant: The real power comes from combining the IoT Agent with Text-to-Speech (TTS).
- Click the icon in the IoT Agent chat window.
- Your browser will ask for microphone permission. Grant it.
- Now, simply speak your command: "Turn on the living room light."
The IoT Agent will understand your command, identify the correct widget and its topic (home/livingroom/light/command), and publish the "ON" payload to the MQTT broker. Your ESP32 will receive the message and turn on the relay, activating your light.
You can try other commands like:
- "Switch off the bedroom fan."
- "Toggle the living room light."
This combination of an affordable ESP32, simple relays, and the intelligent MQTTfy dashboard creates a highly capable and expandable home automation system that you can control from anywhere, with just your voice.